A Comprehensive Framework for AML Risk Assessment
- Steve Marshall

- Aug 2, 2024
- 5 min read
Updated: Nov 17, 2025

Here’s What You’ll Find:
Effective anti-money laundering (AML) risk assessment is critical for detecting and mitigating money laundering and financial crime risk. However, challenges such as poor data quality, outdated risk models, and integration issues can hinder accuracy. Most financial institutions rely on risk assessment AML models that require ongoing refinement.
Here, we explore what AML risk is, key challenges, and a seven-step framework to strengthen AML and customer risk management. We also provide insights on the crucial role of data quality, risk scoring models, and best practices for enhancing AML risk management and regulatory compliance.
What is an AML risk assessment?
An AML risk assessment is a thorough, systematic process designed to detect, evaluate, and mitigate the risks of money laundering and terrorist financing linked to a business relationship. This involves identifying and examining crucial risk factors to understand the AML risk exposure of financial institutions. It also allows them to pinpoint customers with a higher money laundering risk and implement appropriate, risk-based strategies for preventing money laundering. Assessing customer risk is a fundamental component of a financial institution’s overall AML risk evaluation.
By implementing an effective AML risk management framework, financial institutions can proactively identify and assess the likelihood and potential impact of financial crimes within their operations. This enables them to allocate resources, implement proper controls, and prioritize their efforts to effectively manage and mitigate the risks related to financial crime.
Central to the customer AML risk assessment is a risk model that calculates a risk score, or a customer or KYC risk rating, such as high, medium, or low. This risk score or rating provides the AML officer and the business line with a clear image of the risks the customer relationship and activities pose to the institution.
The importance of AML risk assessments
An AML risk assessment enables organizations to adopt a risk-based approach to combat financial crime and meet regulatory expectations. Through thorough assessments, organizations demonstrate their commitment to compliance while efficiently allocating resources and applying enhanced scrutiny to high-risk customers. This strategic approach not only ensures regulatory compliance but also strengthens the organization’s ability to detect and prevent financial crime, safeguarding the integrity of the financial system.
Challenges associated with an AML risk management program

Establishing and supporting an effective AML risk management program comes with various challenges that can affect its success. These challenges need careful consideration and proactive measures to ensure compliance and better manage financial and reputational risks. Key challenges associated with effective AML risk management programs include:
Data quality: AML risk assessment is dependent on accurate and comprehensive customer and transaction data. Inadequate, inconsistent, or inaccurate data can impede the effectiveness of risk assessments.
Infrequent data updates: Regular updates of customer information, such as occupation, industry, address and externally sourced information such as adverse media, are vital to supporting accurate risk assessments and avoiding reliance on obsolete data.
Data integration challenges: Integrating data from various internal and external sources, such as customer databases and transaction records, can be challenging due to differences in formats, systems, and data quality.
Risk scoring models: Risk scoring models must be robust, well-designed, fully documented, and regularly validated and refined to ensure full and effective risk assessments.
Real-time risk detection: The ability to refresh risk profiles in real time based on continuous monitoring activities—including analyzing transactions, screening against watchlists, and assessing changes to customer attributes—is pivotal for dynamic AML risk assessment.
Resource limitations: Comprehensive risk assessments demand competent personnel, a robust technological infrastructure, and access to reliable data sources. These requirements can be challenging to resource constrained organizations.
7 step framework for implementing an effective AML risk assessment program
To set up an effective AML risk assessment program, financial institutions should adhere to a structured framework. This framework can enhance an institution’s risk assessment capabilities and help align it with regulatory requirements. It is important to remember that an AML risk assessment is an iterative process necessitating regular reviews and revisions, and continuous improvement.
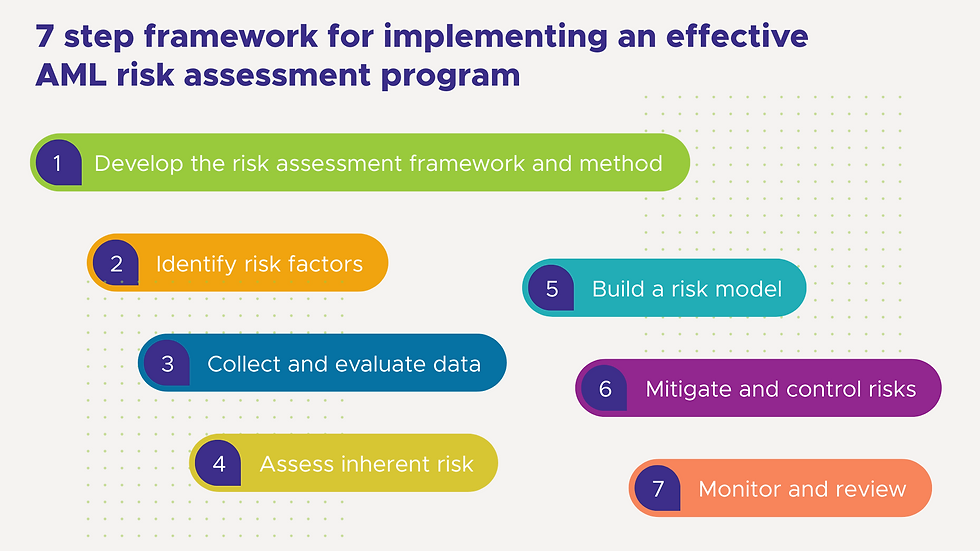
1. Develop the risk assessment framework and method
Outline the risk assessment’s scope, goals, and methodology. Determine the assessment frequency, responsible personnel, and available resources. Ensure compliance with regulatory mandates and industry-leading practices. For help, contact our FinScan AML consulting team.
2. Identify risk factors
Identify the relevant risk factors that apply to your institution, considering aspects like the nature of your business, customer demographics, products and services, delivery channels, geographic locations, transaction monitoring alerts, and watchlist screening results.
3. Collect and evaluate data
Gather relevant data from internal and external sources. This may include customer information, transaction data, external risk indicators, typologies, industry reports, regulatory guidance, and intelligence sources. Ensure data quality and completeness for accurate AML risk assessment.
4. Assess inherent risk
Evaluate each identified AML or KYC risk factor to determine its inherent risk level. Consider the probability and potential impact of money laundering and terrorist financing activities associated with each factor. Use historical data, industry trends, typologies, and regulatory guidance to define the best level of risk assessment.
5. Build a risk model
Develop a risk scoring method to quantify the identified risks. Assign risk scores or ratings to each AML or KYC risk factor based on its significance, likelihood, and potential impact. This aids in prioritizing risks and allocating resources effectively. Include both qualitative and quantitative factors in the scoring process.
6. Mitigate and control risks
Identify and implement suitable risk mitigation measures for each risk profile. These might include enhanced customer due diligence (CDD), transaction monitoring, sanctions screening, staff training, internal controls, and governance practices. Implement controls that are proportional to the risk level and comply with regulatory requirements.
7. Monitor and review
Continuously monitor and review the effectiveness of risk mitigation measures and the overall AML risk assessment framework. Regularly update risk assessments to accommodate changes in the institution’s risk profile, regulatory landscape, emerging risks, and industry best practices. Maintain a feedback loop to improve the risk assessment process over time.
AML risk assessment best practices
To maintain an effective AML risk assessment, financial institutions should implement the following best practices:
Designate a compliance officer: Appoint a dedicated AML compliance officer responsible for overseeing the risk assessment process, ensuring regulatory compliance, and implementing risk mitigation strategies.
Develop internal policies, procedures, and controls: Establish clear AML risk assessment policies that outline risk identification, monitoring, and mitigation processes. Regularly update procedures to align with evolving regulations and emerging financial crime risks.
Train employees on AML risk: Conduct ongoing AML training to educate employees on recognizing suspicious activities, understanding risk factors, and complying with AML policies. A well-trained workforce strengthens risk detection and compliance efforts.
Conduct independent testing and review: Perform periodic AML risk assessment reviews through independent audits or third-party evaluations. This ensures the effectiveness of risk models, validates compliance, and identifies areas for improvement.
By following these best practices, institutions can enhance their AML risk management framework, improve risk detection, and maintain regulatory compliance.

